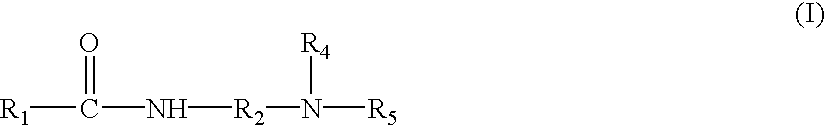US6566313B1 - Shampoo and body wash composition and method of use thereof - Google Patents
Shampoo and body wash composition and method of use thereof Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- US6566313B1 US6566313B1 US09/954,834 US95483401A US6566313B1 US 6566313 B1 US6566313 B1 US 6566313B1 US 95483401 A US95483401 A US 95483401A US 6566313 B1 US6566313 B1 US 6566313B1
- Authority
- US
- United States
- Prior art keywords
- composition
- carbon atoms
- group
- phosphate ester
- alkyl
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime, expires
Links
- 0 [1*]C(=O)N[2*]N([4*])[5*] Chemical compound [1*]C(=O)N[2*]N([4*])[5*] 0.000 description 7
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D1/00—Detergent compositions based essentially on surface-active compounds; Use of these compounds as a detergent
- C11D1/38—Cationic compounds
- C11D1/65—Mixtures of anionic with cationic compounds
- C11D1/652—Mixtures of anionic compounds with carboxylic amides or alkylol amides
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K8/00—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations
- A61K8/18—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition
- A61K8/30—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition containing organic compounds
- A61K8/40—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition containing organic compounds containing nitrogen
- A61K8/42—Amides
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K8/00—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations
- A61K8/18—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition
- A61K8/30—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition containing organic compounds
- A61K8/40—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition containing organic compounds containing nitrogen
- A61K8/44—Aminocarboxylic acids or derivatives thereof, e.g. aminocarboxylic acids containing sulfur; Salts; Esters or N-acylated derivatives thereof
- A61K8/442—Aminocarboxylic acids or derivatives thereof, e.g. aminocarboxylic acids containing sulfur; Salts; Esters or N-acylated derivatives thereof substituted by amido group(s)
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K8/00—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations
- A61K8/18—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition
- A61K8/30—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition containing organic compounds
- A61K8/46—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition containing organic compounds containing sulfur
- A61K8/463—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition containing organic compounds containing sulfur containing sulfuric acid derivatives, e.g. sodium lauryl sulfate
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K8/00—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations
- A61K8/18—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition
- A61K8/30—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition containing organic compounds
- A61K8/55—Phosphorus compounds
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K8/00—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations
- A61K8/18—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition
- A61K8/30—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition containing organic compounds
- A61K8/55—Phosphorus compounds
- A61K8/556—Derivatives containing from 2 to 10 oxyalkylene groups
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61Q—SPECIFIC USE OF COSMETICS OR SIMILAR TOILETRY PREPARATIONS
- A61Q19/00—Preparations for care of the skin
- A61Q19/10—Washing or bathing preparations
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61Q—SPECIFIC USE OF COSMETICS OR SIMILAR TOILETRY PREPARATIONS
- A61Q5/00—Preparations for care of the hair
- A61Q5/02—Preparations for cleaning the hair
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61Q—SPECIFIC USE OF COSMETICS OR SIMILAR TOILETRY PREPARATIONS
- A61Q5/00—Preparations for care of the hair
- A61Q5/12—Preparations containing hair conditioners
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D1/00—Detergent compositions based essentially on surface-active compounds; Use of these compounds as a detergent
- C11D1/02—Anionic compounds
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D1/00—Detergent compositions based essentially on surface-active compounds; Use of these compounds as a detergent
- C11D1/02—Anionic compounds
- C11D1/34—Derivatives of acids of phosphorus
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D1/00—Detergent compositions based essentially on surface-active compounds; Use of these compounds as a detergent
- C11D1/38—Cationic compounds
- C11D1/52—Carboxylic amides, alkylolamides or imides or their condensation products with alkylene oxides
- C11D1/528—Carboxylic amides (R1-CO-NR2R3), where at least one of the chains R1, R2 or R3 is interrupted by a functional group, e.g. a -NH-, -NR-, -CO-, or -CON- group
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a shampoo and/or body wash composition and to a method of use thereof.
- the shampoo or body wash composition is preferably used to both cleanse and condition skin and/or hair treated with the composition.
- the composition of the present invention contains a conditioning complex that is compatible with anionic surfactants and is substantive to skin and/or hair.
- shampoos for cleansing the hair, and body wash compositions for cleaning the skin are commonly formulated with anionic surfactants that produce copious amounts of foam and clean the hair and skin of excess sebum and dirt.
- anionic surfactants also remove the natural protective oils from the skin and hair, leaving the skin and hair dry and/or rough.
- a subsequent separate treatment with a conditioning composition is needed to return the skin and hair to an aesthetically desired state.
- Investigators have sought to develop shampoo and body wash compositions that both cleanse the skin and hair, and leave the skin and hair soft and moisturized.
- U.S. Pat. No. 5,945,093 to Duvel discloses a conditioning shampoo composition containing an anionic surfactant, a cationic surfactant, a silicone conditioning agent and a polymeric suspending agent.
- the cationic surfactant is preferably an acid neutralized amidoamine, that is also disclosed as providing some conditioning properties.
- a disadvantage of this formulation is that when the amidoamine is neutralized with the acids disclosed therein, the resultant quaternary salt is not substantive to skin and hair, and is easily rinsed, leaving little or no residual softness and/or smoothness.
- the present invention provides a shampoo and/or body wash composition which contains a conditioning complex that is strongly substantive to the skin and hair, and does not leave a greasy feel to the skin or hair.
- the composition can also preferably be formulated to be visually transparent.
- the conditioning complex also permits the composition to be formulated to the intrinsic pH of healthy skin and hair, which provides the treated skin and hair with a cosmetically desirable smooth, soft and moisturized feel.
- the present invention relates to a shampoo or body wash composition that can be used to both clean and condition the skin or hair.
- the composition contains from about 1 weight percent to about 40 weight percent, based on the total weight of the composition of at least one anionic surfactant; a conditioning complex, and at least about 40 weight percent of water.
- the conditioning complex is formed from at least
- R 6 is an alkylene group having from about 2 to about 4 carbon atoms
- R 7 is an alkyl group having from about 8 to about 22 carbon atoms
- n is a number ranging from 1 to about 30
- R 8 is hydrogen, an R 7 (OR 6 ) n — group, an alkyl group having from 1 to about 5 carbon atoms, a hydroxyalkyl group having from 1 to about 5 carbon atoms, an alkali metal, alkaline earth metal, diethanolamine, or ammonium group
- the amount of phosphate ester added to the composition is such that a solution consisting of water, the alkyl amidoamine in the amount used in the shampoo or body wash composition, and the phosphate ester in the amount used in the shampoo or body wash composition, results in an aqueous pH ranging from about 4 to about 6.
- the composition has a pH of from about 4 to about 6.
- the present invention also provides a method of treating skin or hair comprising contacting the skin or hair with the composition of the present invention.
- the present invention is also directed to a water-dispersible conditioning complex formed by the steps that include combining the alkyl amidoamine of (i) and the phosphate ester of (ii) to form a mixture, where the molar ratio of the phosphate ester to the alkyl amidoamine ranges from about (1:1) to about (3:1).
- the shampoo or body wash composition of the present invention cleans the skin and/or hair, while also having conditioning properties.
- shampoo or body wash composition it is meant any composition useful for cleaning the skin and/or hair.
- cleaning it is meant removing substances such as dirt and sebum from hair and/or skin.
- conditioning it is meant that skin treated with the composition is preferably smooth, moisturized, and/or soft, and hair treated with the composition is preferably soft, smooth, and/or free of tangles.
- the composition of the present invention contains a special conditioning complex and an anionic surfactant.
- the conditioning complex surprisingly enhances the quantity and/or quality of foam produced by the anionic surfactant, while also providing conditioning benefit to the skin or hair.
- Other benefits of the composition of the present invention include reduced irritation due to excessive defatting of the skin and scalp.
- the composition may also, if desired, be formulated as a transparent formulation, semi-transparent, or opaque formulation.
- the conditioning complex of the present invention is preferably water dispersible and is formed from at least a tertiary alkyl amidoamine and a phosphate ester.
- water-dispersible it is meant that the conditioning complex is dispersible in the shampoo or body wash composition of the present invention, but preferably not dissolved in water.
- formed from at least it is meant that at least the alkyl amidoamine and the phosphate ester are combined to form the conditioning complex.
- other optional compounds such as water are present when the conditioning complex is formed.
- tertiary alkyl amidoamines are strongly alkaline materials that are generally neutralized with acids to form cationic conditioning compounds useful in rinse-off hair conditioners.
- tertiary alkyl amidoamines are neutralized with water-soluble acids, such as citric acid, the alkyl amidoamine becomes a water-soluble cationic quaternary conditioner.
- These conditioners although having good substantivity to the hair or skin, are not deposited on the hair and skin in a sufficient amount, resulting in a feeling of softness, but no perceptible emollience (i.e., smoothness).
- the alkyl amidoamine When the tertiary alkyl amidoamine is neutralized with a high molecular weight fatty acid, such as stearic acid, the alkyl amidoamine becomes an oil-soluble cationic quaternary emulsifier, having good substantivity to the skin or hair, but very poor rinseability. This results in the hair feeling heavy and/or greasy and the skin feeling greasy and or coated after treatment with this compound.
- a high molecular weight fatty acid such as stearic acid
- phosphate esters can be used to neutralize tertiary alkyl amidoamines to form a cationic conditioning complex that has good substantivity to hair and skin, can be deposited on the hair and skin in an adequate amount, and can also be adequately rinsed from the skin or hair, leaving hair soft and manageable and skin smooth and moisturized.
- the conditioning complex of the present invention is compatible with anionic surfactants typically used in shampoo or body wash compositions. Additionally, it has unexpectedly been discovered that while most cationic conditioning compounds adversely effect the foaming properties of anionic surfactants, the conditioning complex of the present invention actually enhances the foam volume and foam quality (e.g., creaminess) of the anionic surfactant.
- Tertiary alkyl amidoamines useful in the present invention are tertiary amines where at least one of the substituents of the amine is R 1 CONHR 2 —, where R 1 is an alkyl group having from about 9 to about 21 carbon atoms, and R 2 is an alkylene group having from 1 to about 8 carbon atoms.
- the tertiary alkyl amidoamine is preferably water dispersible.
- the alkyl amidoamine used to form the conditioning complex is preferably in an amount to provide some conditioning benefit to the skin or hair.
- the amount of alkyl amidoamine used to form the conditioning complex is at least about 0.01 weight percent, more preferably from about 0.1 weight percent to about 4 weight percent, and most preferably from about 0.2 weight percent to about 1 weight percent, based on the total weight of the shampoo or body wash composition.
- Preferred tertiary alkyl amidoamines include those of the following formula I:
- R 1 is an alkyl group having from about 9 to about 21 carbon atoms
- R 2 is an alkylene group having from 1 to about 8 carbon atoms
- R 4 and R 5 are independently an alkyl group having 1 to about 5 carbon atoms, or a hydroxyalkyl group having from 1 to about 5 carbon atoms.
- the alkyl groups and/or alkylene groups of R 1 to R 5 may be linear, branched, saturated, or unsaturated or combinations thereof.
- the R 1 does not have to be solely or primarily of one chain length such as lauryl (C 12 ) or stearyl (C 18 ). Rather, R 1 may be a mixture of chain lengths.
- Such alkyl amidoamine compounds may be conveniently prepared from naturally occurring materials such as tallow, coconut oil, soya oil, or combinations thereof, or from synthetically produced mixtures.
- R 1 is an alkyl group having from about 12 to about 20 carbon atoms and more preferably from about 14 to about 18 carbon atoms
- R 2 is an alkylene group having from about 2 to about 4 carbon atoms, and more preferably from about 2 to about 3 carbon atoms
- R 4 and R 5 are independently methyl, ethyl, propyl, or combinations thereof.
- alkyl amidoamines useful in the present invention include lauramidopropyldimethylamine, stearamidopropyldimethylamine, isosteararnidopropyldimethylamine, stearamidopropyldiethanolamine, stearamidoethyldiethanolamine, stearamidoethyldiethylamine, cocamidopropyldimethylamine, wheat germ-amidopropyldimethylamine, palmitamidopropyldimethylamine, soyamidopropyldimethylamine, myristamidopropyldimethylamine, oleamidopropyldimethylamine, ricinoleamidopropyl dimethylamine, or combinations thereof.
- the tertiary alkyl amidoamine is isostearamidopropyl dimethylamine, oleamidopropyldimethylamine, ricinoleamidopropyl dimethylamine,
- the above alkyl amidoamines are commercially available for example as LEXAMINE 0-13 or LEXAMINE S-13 supplied by Inolex Chemical Div., Philadelphia, Pa. and as MACKINE 201 or MACKINE 401 supplied by McIntyre Group Ltd.
- the phosphate ester of the present invention is a phosphate ester of an alkoxylated ether of a fatty alcohol where the fatty alcohol has from about 8 to about 22 carbon atoms and the alkoxylated ether preferably has from 1 to about 30 alkoxy groups, where the alkoxy groups have from about 2 to about 4 carbon atoms.
- the phosphate ester also has at least one acidic hydrogen for forming a complex with the alkyl amidoamine.
- the phosphate ester includes at least one compound of formula II:
- R 6 is an alkylene group having from about 2 to about 4 carbon atoms
- R 7 is an alkyl group having from about 8 to about 22 carbon atoms
- n is a number ranging from 1 to about 30
- R 8 is hydrogen, an R 7 (OR 6 ) n — group, an alkyl group having from 1 to about 5 carbon atoms, a hydroxyalkyl group having from 1 to about 5 carbon atoms, an alkali metal, alkaline earth metal, diethanolamine, or ammonium group.
- the alkyl groups and/or hydroxyalkyl groups of R 7 to R 8 may be linear, branched, saturated, or unsaturated or combinations thereof.
- the carbon portion of the (OR 6 ) group may be linear or branched, and/or R 7 of formula II may be a mixture of chain lengths, such as described in connection with R 1 of formula I.
- (OR 6 ) is a C 2 to C 3 alkoxy group and more preferably a mixture of ethoxy and propoxy groups where the number of ethoxy groups ranges on average from about 5 to about 15, and more preferably from about 7 to about 11, and the number of propoxy groups ranges on average from about 1 to about 10 and more preferably from about 3 to about 6,
- R 7 is an alkyl group having from about 12 to about 20 carbon atoms and more preferably from about 14 to about 18 carbon atoms
- n is a number ranging from about 5 to about 25 and more preferably from about 10 to about 20
- R 8 is hydrogen, or an R 7 (OR 6 ) n — group, or combinations thereof.
- the phosphate ester is a mixture of monoester, where R 8 is hydrogen, and a diester where R 8 is a R 7 (OR 6 ) n — group.
- the weight ratio of monoester to diester is from about (1:10) to about (10:1) and more preferably from about (1:2) to about (2:1).
- (OR 6 ) n is a mixture of ethoxy and propoxy groups where the average number of ethoxy groups is from about 7 to about 12 and the average number of propoxy groups is from about 2 to about 6 for each R 7 (OR 6 ) n — group.
- R 7 is an alkyl group having from about 14 to 18 carbon atoms or mixtures thereof.
- a most preferred phosphate ester useful in the present invention is an alkoxylated ether of cetyl alcohol having on average 5 propoxy groups and 10 ethoxy groups.
- a phosphate ester is known as PPG-5-Ceteth-10 Phosphate and is commercially available from such suppliers as Croda, Inc. located in New Jersey under the name Crodafos SG.
- PPG-5-Ceteth-10 Phosphate is a mixture of the phosphate monoester and diester of propoxylated ethoxylated ether of cetyl alcohol, and has the general formulae:
- R represents:
- the amount of phosphate ester used to form the conditioning complex is preferably in an amount that a solution containing just water, the alkyl amidoamine in the amount used in the shampoo or body wash composition, and the phosphate ester results in an aqueous pH that is about the pH of healthy skin and hair.
- this pH ranges from about 4 to about 6, more preferably from about 4.5 to about 5.5 and most preferably about 5.
- the amount of phosphate ester needed to achieve this pH will depend on the number of acidic hydrogens on the phosphate ester, generally the ratio of moles of phosphate ester to the moles of alkyl amidoamine used to form the conditioning complex should preferably be from about (1:1) to about (3:1), and more preferably from about (1.5:1) to about (2:1).
- the moles of phosphate ester used to form the conditioning complex is preferably in an excess molar amount compared to the molar amount needed to neutralize the alkyl amidoamine. Accordingly, it is believed that not all the phosphate ester present in the shampoo or body wash composition complex complexes with the alkyl amidoamine in the conditioning complex.
- the pH of the conditioning complex is preferably prepared to be about the pH of healthy skin and hair, the film deposited on the skin and hair by the shampoo or body wash composition produces a soft, moisturized, emollient feel on the skin or hair.
- the conditioning complex could also be used in conditioners.
- the shampoo or body wash composition also contains at least one anionic surfactant.
- Any anionic surfactant may be used that is dermatologically compatible with skin or hair.
- Dermatologically compatible it is meant that the compound does not cause irritation when applied to the skin for the purpose of cleaning and then is subsequently removed within about 30 minutes of application.
- the anionic surfactant is preferably present at a level of from about 1 weight percent to about 40 weight percent, more preferably from about 5 weight percent to about 30 weight percent, and most preferably from about 5 weight percent to about weight percent, based on the total weight of the composition.
- Anionic surfactants useful in the present invention are well known and include for example alkyl sulfates, alkyl ether sulfates, alkyl ether carboxylates, acyl isethionates, acyl sarcosinates, acyl taurines, or alkali metal, ammonium, or alkanolammonium salts thereof, or combinations thereof.
- the alkyl or acyl groups of these surfactants contain from about 10 to about 20 carbon atoms per alkyl or acyl group, more preferably from about 12 to about 18 carbon atoms per alkyl or acyl group.
- the alkyl or acyl groups may be linear, branched, saturated or unsaturated or combinations thereof. More preferably, the alkyl or acyl groups are linear.
- the anionic surfactant includes at least one alkyl sulfate, alkyl ether sulfate, salts thereof, or combinations thereof.
- These surfactants have respectively the general formulae:
- R 9 is an alkyl group of about 10 to about 20 carbon atoms, more preferably about 12 to about 18 carbon atoms, x is 1 to about 10, more preferably 1 to about 4, and M + is a water-soluble cation such as ammonium, an alkali metal salt such as sodium or potassium, or an alkanolammonium salt such as triethanolamine.
- preferred anionic surfactants useful in the present invention include ammonium lauryl sulfate, sodium lauryl sulfate, ammonium laureth sulfate (preferably with 1 to about 3 moles ethylene oxide), sodium laureth sulfate (with preferably 1 to about 3 moles ethylene oxide), or combinations thereof.
- the conditioning complex and anionic surfactant are formulated with water as a carrier to form the shampoo or body wash conditioning composition of the present invention.
- Water is preferably present in an amount of at least about 40 weight percent, more preferably from about 50 weight percent to about 90 weight percent, and most preferably from about 60 weight percent to about 80 weight percent, based on the total weight of the composition.
- the composition may also contain other carriers such as organic solvents.
- organic solvents include C 2 to C 6 monoalcohols, such as ethanol, propanol, isopropanol, or tert-butyl alcohol; ethylene glycol; ethylene glycol monomethyl ether; ethylene glycol monoethyl ether; ethylene glycol monobutyl ether; ethylene glycol monoethyl ether acetate; propylene glycol; propylene glycol monomethyl ether; dipropylene glycol monomethyl ether; glycerol; or diethylene glycol; or combinations thereof.
- the shampoo or body wash composition of the present invention is formulated as a monoalcohol-free composition.
- the shampoo or body wash composition of the present invention is at a pH that is dermatologically compatible with skin and hair.
- the pH of the shampoo or body wash composition is from about 4 to about 6, more preferably from about 4.5 to about 5.5, and most preferably about 5. If necessary, the pH of the shampoo or body wash composition may be adjusted with any of a number of commonly used cosmetic ingredients.
- Suitable pH adjusters include acids for decreasing the pH including inorganic acids such as phosphoric acid, nitric acid, or hydrochloric acid, or organic acids such as citric acid or tartaric acid; or basic compounds for increasing the pH, including organic amines such as triethanolamine, ethanolamine, or aminomethylpropanol, alkali metal or alkaline earth metal hydroxides such as sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide; ammonium hydroxide, basic amino acids such as arginine, sodium hydroxymethylglycinate, or combinations thereof.
- the pH of the shampoo or body wash composition should not be adjusted with either of the components of the conditioning complex, the alkyl amidoamine, or the phosphate ester, as this would alter the ratio of these two components.
- the shampoo or body wash composition contains an amphoteric surfactant, zwitterionic surfactant, or combinations thereof.
- the total amount of amphoteric and zwitterionic surfactant is from 0 to about 5 weight percent and more preferably from about 1 to about 4, based on the total weight of the composition.
- amphoteric or zwitterionic surfactants for use in the present invention include alkyl betaines, alkylamidobetaines, aminopropionates, aminoglycinates, imidazolinium betaines, sulfobetaines or combinations thereof.
- a preferred zwitterionic surfactant of the present invention includes compounds having formula III:
- R 11 is an alkyl or alkenyl group containing from about 10 to about 20 carbon atoms or a R 13 —CONH—(CH 2 ) p group, where R 13 is an alkyl or alkenyl group containing from about 10 to about 20 carbon atoms and p is a number of from about 2 to about 5, and R 10 and R 12 are alkyl groups containing from 1 to about 5 carbon atoms or hydroxyalkyl groups containing from about 2 to about 4 carbon atoms.
- Preferred amphoteric surfactants includes compounds having formula IV:
- R 11 is an alkyl or alkenyl group containing from about 10 to about 20 carbon atoms or a R 13 —CONH—(CH 2 ) p group, where R 13 is an alkyl or alkenyl group containing from about 10 to about 20 carbon atoms and p is a number of from about 2 to about 5, and R 14 is an alkyl group containing from 1 to about 5 carbon atoms or a hydroxyalkyl group containing from about 2 to about 4 carbon atoms.
- amphoteric or zwitterionic surfactants useful in the present invention include sodium 3-dodecyl-aminopropionate, sodium 3-dodecylaminopropane sulfonate, sodium lauroamphoacetate, coco dimethyl carboxymethyl betaine, cocoamidopropyl betaine, cocobetaine, lauryl amidopropyl betaine, oleyl betaine, lauryl dimethyl carboxymethyl betaine, lauryl dimethyl alphacarboxyethyl betaine, cetyl dimethyl carboxymethyl betaine, lauryl bis-(2-hydroxyethyl) carboxymethyl betaine, stearyl bis-(2-hydroxypropyl) carboxymethyl betaine, oleyl dimethyl gamma-carboxypropyl betaine, lauryl bis-(2-hydroxypropyl)alpha-carboxyethyl betaine, oleamidopropyl betaine, coco dimethyl sulfopropyl betaine,
- composition of the present invention may be included in the composition of the present invention, as long as the basic properties of the shampoo or body wash composition are not adversely affected.
- optional cosmetic additives may be found, for example, in the International Cosmetic Ingredients Dictionary, 7th Edition, 1997, published by the CTFA in Washington D.C.
- these optional components in total, are present in an amount of from 0 to 20 weight percent, and more preferably from about 0.1 to about 12 weight percent, based on the total weight of the composition.
- optional additive components include, but are not limited to, one or more surfactants such as nonionic surfactants or cationic surfactants, protein hydrolyzates, other conditioning agents, inorganic electrolyte salts or combinations thereof.
- surfactants such as nonionic surfactants or cationic surfactants, protein hydrolyzates, other conditioning agents, inorganic electrolyte salts or combinations thereof.
- surfactants that are typically used in shampoo or body wash compositions may optionally be added to the composition of the present invention such as nonionic and/or cationic surfactants.
- these surfactants are present in an amount of no more than about 10 weight percent, more preferably in an amount of 0 weight percent to about 5 weight percent, and most preferably in an amount of about 0.01 weight percent to about 3 weight percent, based on the total weight of the composition.
- Surfactants may include for example, nonionic surfactants present in an amount preferably ranging from 0 weight percent to about 10 weight percent and more preferably from 0 weight percent to about 2 weight percent, based on the total weight of the composition.
- nonionic surfactants include for example alkyl polyglycosides, alkyl oligoglycosides, ethoxylated fatty alcohols, sorbitan esters, or alkanolamides such as cocamide MEA, cocamide DEA, soyamide DEA, lauramide DEA, lauramide MEA, lauramide MIPA, oleamide MIPA, ricinoleamide DEA, stearamide MEA, stearamide DEA, isostearamide MEA, isostearamide DEA, myristamide MEA, lauramide MEA, capramide DEA, stearamide DEA, oleylamide DEA, myristamide DEA, or tallowamide DEA, or combinations thereof.
- alkanolamides such as cocamide MEA, cocamide DEA, soyamide DEA, lauramide DEA, lauramide MEA, lauramide MIPA, oleamide MIPA, ricinoleamide DEA,
- Surfactants may also be cationic surfactants present in an amount preferably ranging from 0 weight percent to about 5 weight percent and more preferably from 0 weight percent to about 1 weight percent, based on the total weight of the composition.
- cationic surfactants include quaternary ammonium compounds.
- a more extensive list of surfactants are described for example in U.S. Pat. No. 5,955,066, and McCutcheon's Emulsifiers & Detergents, North American Edition and International Edition, 1999 Annuals, published by McCutcheon's Division, MC Publishing Company, Glen Rock, N.J. (1999). The complete disclosure of these documents are incorporated herein by reference in their entireties.
- Protein hydrolyzates may also be present in the composition in an amount of up to about 2.0 weight percent, based on the total weight of the composition.
- protein hydrolyzates include elastin, collagen, keratin, milk protein, soya protein, or wheat protein hydrolyzates, or condensation products thereof with fatty acids, or quaternized protein hydrolyzates, or combinations thereof.
- conditioning agents suitable for use in the present invention include compounds that soften, strengthen, add shine and/or detangle the hair, or soften and/or moisturize skin, such as phospholipids (e.g., soya lecithin, egg lecithin or kephalins), silicone compounds, proteins, amino acids, or combinations thereof.
- phospholipids e.g., soya lecithin, egg lecithin or kephalins
- silicone compounds include, for example, polyalkylsiloxanes, polyarylsiloxanes, polyarylalkylsiloxanes, polyethersiloxanes or silicone resins.
- these conditioning agents are present in the composition in an amount of no more than about 1 weight percent, more preferably from 0 weight percent to about 0.75 weight percent and most preferably from 0 weight percent to about 0.1 weight percent, based on the total weight of the composition.
- Inorganic electrolyte salts may also be added to the composition of the present invention in an amount of from 0 weight percent to about 2 weight percent, based on the total weight of the composition. Such electrolyte salts may be added, for example, to thicken the composition.
- Inorganic electrolyte salts that may be used are any water-soluble alkali metal, ammonium or alkaline earth metal salt, for example the fluorides, chlorides, bromides, sulfates, phosphates, nitrates or hydrogen carbonates, providing that they are soluble in water at 20° C. in a quantity of at least 1 percent by weight. Sodium chloride and magnesium chloride are especially preferred.
- the shampoo or body wash composition of the present invention may also contain as optional additive components, one or more sequestrants such as ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA), or phosphonic acids; fragrances; other nonactive ingredients such as panthenol, allantoin, pyrrolidone carboxylic acids or salts thereof; plant extracts; vitamins such as Vitamins A, B, C, or E, or combinations thereof; preservatives such methylchloroisothiazolinone, methylisothiazolinone, or diazolidinyl urea or combinations thereof; humectants, such as sorbitol, glycerin, propylene glycol, or butylene glycol or combinations thereof; light stabilizers; dyes; pearlescers, such as ethylene glycol monostearate or distearate; antioxidants; thickeners such as polysaccharides, including for example, xanthan gum, guar gum, agar gum, alginates, tylose
- a method for treating skin or hair using the composition of the present invention.
- the composition is preferably applied to skin or hair that has first been wetted with water.
- the composition is preferably rinsed from the skin or hair with water to remove any undesirable substances such as dirt or sebum.
- the composition has the advantage of both simultaneously cleaning and conditioning the skin or hair.
- composition of the present invention is preferably prepared by adding the anionic surfactant to water and adjusting the pH to about 4 to about 6. Following adjustment of the pH, the alkyl amidoamine and phosphate ester are added to the surfactant solution with mixing.
- the amidoamine or phosphate ester are solids at room temperature, they may be warmed until melted and added in melted form to the surfactant solution.
- the weight percentage listed in each of the following examples represents the amount of each ingredient present in the shampoo or body wash composition.
- the compositions were prepared by combining the ingredients in the order of appearance in Table 1 below, except that in Ex.2, the stearic acid was melted and mixed with the amidoamine prior to being added to the surfactant solution:
- compositions of Examples 3 to 5 are transparent liquids having a pH of about 5.0 and a viscosity of about 5,000 to about 10,000 centipoise.
- the compositions of Examples 3 to 5 exhibited excellent storage stability, showing no phase separation or ingredient precipitation after storage for several weeks at about 4° C., about 25° C., and about 45° C.
- the compositions of Examples 1 to 5 were further evaluated as shown below:
- the foam quantity and conditioning benefit in the table above was evaluated by applying the composition to wetted skin and hair and subsequently rinsing the composition with water.
- the foam quantity and conditioning benefit was qualitatively ranked as either excellent, good, or poor.
- the composition of the present invention (Examples 3 to 5) produced more foam and more conditioning benefit in comparison to compositions of comparative Examples 1 and 2, where the alkyl amidoamine was neutralized with citric acid and stearic acid, respectively.
Abstract
Description
| TABLE 1 |
| Compositions Evaluated |
| Ex. 1 | Ex. 2 | ||||
| Ingredients | (comp) | (comp) | Ex. 3 | Ex. 4 | Ex. 5 |
| Water | qs to 100 | qs to 100 | qs to 100 | qs to 100 | qs to 100 |
| Sodium Laureth-2 Sulfate | 30 | 30 | 30 | 20 | 20 |
| 27 wt % active | |||||
| Cocamidopropyl Betaine | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 0 |
| 30 wt % active | |||||
| Oleamidopropyl Betaine | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 |
| Methylchloroisothiazolinone | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| Methylisothiazolinone | qs pH 5 | qs pH 5 | qs pH 5 | qs pH 5 | qs pH 5 |
| Citric Acid | |||||
| PPG-5-Ceteth-10-Phosphate1 | 0 | 0 | 0.70 | 0.68 | 0.70 |
| Stearic Acid | 0 | 0.4 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Isostearamidopropyl | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0 | 0 |
| Dimethylamine2 | |||||
| Rocinoleamidopropyl | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.32 | 0 |
| Dimethylamine3 | |||||
| Oleamidopropyl | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.30 |
| Dimethylamine4 | |||||
| Sodium Chloride | 1.20 | 1.20 | 1.20 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| 1Crodafos SG, supplied by Croda, Inc. | |||||
| 2Mackine 401, supplied by McIntyre. | |||||
| 3Mackine 201, supplied by McIntyre | |||||
| 4Lexamine 0-13, supplied by Inolex. | |||||
| TABLE 2 |
| Properties of Examples 1 to 5 |
| Ex. 1 | Ex. 2 | ||||
| Property | (comp.) | (comp.) | Ex. 3 | Ex. 4 | Ex. 5 |
| Appearance | Clear | Opaque | Clear | Clear | Clear |
| (visual) | |||||
| Foam | Good | Poor | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent |
| quantity | |||||
| Conditioning | Good | Poor | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent |
| benefit to skin | (waxy/ | ||||
| and hair | greasy) | ||||
Claims (11)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US09/954,834 US6566313B1 (en) | 2000-09-15 | 2001-09-17 | Shampoo and body wash composition and method of use thereof |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US23320800P | 2000-09-15 | 2000-09-15 | |
| US09/954,834 US6566313B1 (en) | 2000-09-15 | 2001-09-17 | Shampoo and body wash composition and method of use thereof |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| US6566313B1 true US6566313B1 (en) | 2003-05-20 |
Family
ID=26926709
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US09/954,834 Expired - Lifetime US6566313B1 (en) | 2000-09-15 | 2001-09-17 | Shampoo and body wash composition and method of use thereof |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US6566313B1 (en) |
Cited By (29)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6780825B2 (en) * | 2001-02-06 | 2004-08-24 | Playtex Products, Inc. | Cleansing compositions with milk protein and aromatherapy |
| WO2004104147A1 (en) * | 2003-05-22 | 2004-12-02 | Reckitt Benckiser N.V. | Aqueous cleaning compositions |
| US20050276778A1 (en) * | 2004-04-19 | 2005-12-15 | Wsp Chemicals & Technology, Llc | Water soluble polymer complexes with surfactants |
| US20060002871A1 (en) * | 2004-06-30 | 2006-01-05 | Goldstein Mindy S | Cosmetic compositions and methods comprising rhodiola rosea |
| US20060034778A1 (en) * | 2002-09-27 | 2006-02-16 | Yoshinhisa Kitano | Packaged personal care compositions |
| US20080008672A1 (en) * | 2006-07-07 | 2008-01-10 | Ajinomoto Co. Inc. | Low temperature-stable creamy wash composition |
| US20080028986A1 (en) * | 2006-06-12 | 2008-02-07 | Rhodia, Inc. | Hydrophilized substrate and method for hydrophilizing a hydrophobic surface of a substrate |
| WO2008047248A2 (en) * | 2006-10-19 | 2008-04-24 | L'oreal | Aqueous delivery system for water-insoluble materials |
| US20080176977A1 (en) * | 2007-01-23 | 2008-07-24 | John Pastorello | Burst resistant bubbles |
| US20080312341A1 (en) * | 2007-06-12 | 2008-12-18 | Rhodia Inc. | Mono-, di- and polyol phosphate esters in personal care formulations |
| US20080312118A1 (en) * | 2007-06-12 | 2008-12-18 | Rhodia Inc. | Hard surface cleaning composition with hydrophilizing agent and method for cleaning hard surfaces |
| US20080311055A1 (en) * | 2007-06-12 | 2008-12-18 | Rhodia Inc. | Mono-, di- and polyol alkoxylate phosphate esters in oral care formulations and methods for using same |
| US20090023618A1 (en) * | 2007-07-20 | 2009-01-22 | Rhodia Inc. | Method for recovering crude oil from a subterranean formation |
| US20100008885A1 (en) * | 2008-07-09 | 2010-01-14 | Susan Daly | Methods and kits imparting benefits to keratin-containing substrates |
| WO2010031689A1 (en) * | 2008-09-17 | 2010-03-25 | Henkel Ag & Co. Kgaa | All-purpose cleaner with improved cleaning performance in diluted application |
| US20100260696A1 (en) * | 2007-08-02 | 2010-10-14 | Clariant Finance (Bvi) Limited | Aqueous Compositions Containing Alkoxylated Phosphoric Acid Triesters |
| US7919449B2 (en) | 2007-06-12 | 2011-04-05 | Rhodia Operations | Detergent composition with hydrophilizing soil-release agent and methods for using same |
| US20120145172A1 (en) * | 2009-08-31 | 2012-06-14 | Kobo Products, Inc. | Surface modified pigment |
| US20150094383A1 (en) * | 2012-04-24 | 2015-04-02 | Stepan Company | Synergistic surfactant blends |
| CN105906526A (en) * | 2016-04-25 | 2016-08-31 | 中国石油集团渤海钻探工程有限公司 | Technology for preparing acidized self-diverting agent by batch process |
| US9622951B2 (en) | 2012-10-29 | 2017-04-18 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Personal care compositions |
| US20190216697A1 (en) * | 2018-01-18 | 2019-07-18 | Nohbo,LLC | Hygiene product pod and methods of using same |
| CN111225655A (en) * | 2017-08-25 | 2020-06-02 | 荷兰联合利华有限公司 | Personal cleansing compositions |
| CN111246837A (en) * | 2017-08-25 | 2020-06-05 | 荷兰联合利华有限公司 | Personal cleansing compositions |
| US20210000724A1 (en) * | 2019-07-05 | 2021-01-07 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Personal care cleaning compositions |
| WO2021104844A1 (en) | 2019-11-26 | 2021-06-03 | Unilever Ip Holdings B.V. | Cleansing composition |
| US11045397B2 (en) | 2019-11-06 | 2021-06-29 | Nohbo, LLC | Hygiene product pod and methods of using same |
| US11453598B2 (en) | 2009-08-31 | 2022-09-27 | Colgate-Palmolive Company | Surface modified pigment |
| WO2024002647A1 (en) | 2022-06-30 | 2024-01-04 | Unilever Ip Holdings B.V. | Stable wash composition with unsaturated zwitterionic surfactant |
Citations (43)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3990991A (en) | 1974-02-01 | 1976-11-09 | Revlon, Inc. | Shampoo conditioner formulations |
| US4298494A (en) | 1979-03-27 | 1981-11-03 | Lever Brothers Company | Shampoo |
| US4321256A (en) | 1979-07-19 | 1982-03-23 | Lever Brothers Company | Shampoo containing a polyglycol-polyamine condensation resin and a phosphate ester |
| US4321156A (en) | 1977-03-30 | 1982-03-23 | S. C. Johnson & Son, Inc. | Shampoo composition |
| US4479893A (en) | 1981-10-28 | 1984-10-30 | Kao Corporation | Shampoo composition containing phosphoric acid ester and organic silicon derivative |
| US4701322A (en) | 1980-04-21 | 1987-10-20 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Conditioning shampoo |
| US4722837A (en) | 1984-05-29 | 1988-02-02 | Derma-Cure, Inc. | Medicated shampoo composition |
| US4726945A (en) | 1986-06-17 | 1988-02-23 | Colgate-Palmolive Co. | Hair rinse conditioner |
| US4728457A (en) | 1986-08-25 | 1988-03-01 | The Proctor & Gamble Company | Process for making a silicone-containing shampoo |
| US4741855A (en) | 1984-11-09 | 1988-05-03 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Shampoo compositions |
| US4906460A (en) | 1988-08-05 | 1990-03-06 | Sorenco | Additive for hair treatment compositions |
| US4938953A (en) | 1988-08-09 | 1990-07-03 | The Upjohn Company | Self-preserving conditioning shampoo formulation |
| US5059414A (en) | 1988-07-01 | 1991-10-22 | Shiseido Co. Ltd. | Multi-phase high viscosity cosmetic products |
| US5077041A (en) | 1989-04-14 | 1991-12-31 | Kao Corporation | Shampoo composition |
| US5078990A (en) | 1990-07-13 | 1992-01-07 | Helene Curtis, Inc. | Shampoos and conditioning shampoos having increased capacity for incorporation of conditioning agents and removal of hair soil |
| US5091171A (en) | 1986-12-23 | 1992-02-25 | Yu Ruey J | Amphoteric compositions and polymeric forms of alpha hydroxyacids, and their therapeutic use |
| US5120531A (en) | 1990-04-06 | 1992-06-09 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Hair styling conditioners |
| US5137715A (en) | 1990-12-07 | 1992-08-11 | Helene Curtis, Inc. | Hair shampoo-conditioner composition |
| US5145607A (en) | 1990-06-19 | 1992-09-08 | Takasago International Corporation (U.S.A.) | Optically clear conditioning shampoo comprising anionic and cationic surfactants |
| US5217711A (en) | 1991-10-16 | 1993-06-08 | Mariana De Oliveira | Hair care system |
| US5227156A (en) | 1992-04-14 | 1993-07-13 | Amway Corporation | Use of zinc compounds to stabilize a thiazolinone preservative in an anti-dandruff shampoo |
| US5328685A (en) | 1993-03-30 | 1994-07-12 | Helene Curtis, Inc. | Clear conditioning composition |
| US5334325A (en) | 1991-01-23 | 1994-08-02 | S. C. Johnson & Son, Inc. | Delayed-gelling, post-foaming composition based upon alkoxylated alkyl phosphate ester surfactants |
| US5346639A (en) | 1994-01-11 | 1994-09-13 | Geoff Hatfield | Spray dispensed shampoo |
| US5384114A (en) | 1992-03-27 | 1995-01-24 | Helene Curtis, Inc. | Opacifier for water-based compositions |
| US5393519A (en) | 1992-03-27 | 1995-02-28 | Helene Curtis, Inc. | Shampoo compositions |
| US5456863A (en) | 1992-04-15 | 1995-10-10 | Helene Curtis, Inc. | Conditioning shampoo composition and method of preparing and using the same |
| US5565216A (en) | 1993-07-21 | 1996-10-15 | Carson Products Company | Hair relaxer compositions |
| US5578560A (en) | 1992-10-14 | 1996-11-26 | Henkel Corporation | Water-containing detergent mixtures comprising oligoglycoside surfactants |
| US5587154A (en) | 1992-03-27 | 1996-12-24 | Helene Curtis, Inc. | Shampoo compositions and suspending agent therefor |
| US5610187A (en) | 1994-08-05 | 1997-03-11 | Witco Corporation | Biodegradable quaternary hair and skin conditioners |
| US5618522A (en) | 1995-01-20 | 1997-04-08 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Emulsion compositions |
| US5658558A (en) | 1994-10-03 | 1997-08-19 | Rohm And Haas Company | Hair styling compositions and method of enhancing the performance of hair fixative resins |
| US5683683A (en) | 1995-09-21 | 1997-11-04 | Helene Curtis, Inc. | Body wash composition to impart conditioning properties to skin |
| US5783200A (en) | 1997-01-21 | 1998-07-21 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Personal cleansing compositions |
| US5883068A (en) | 1994-10-04 | 1999-03-16 | Henkel Kommanditgesellschaft Auf Aktien | Pumpable water-containing surfactant concentrates |
| US5925615A (en) | 1998-03-06 | 1999-07-20 | Nu Skin International, Inc. | Awapuhi (Zingiber zerumbet) -containing hair cleansing and conditioning compositions |
| US5945093A (en) | 1998-04-22 | 1999-08-31 | Amway Corporation | Conditioning shampoo |
| US5955066A (en) | 1995-10-16 | 1999-09-21 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Conditioning shampoo compositions having improved stability |
| US5977038A (en) | 1996-08-05 | 1999-11-02 | Helene Curtis, Inc. | Shampoo compositions and method |
| US6010689A (en) | 1997-04-21 | 2000-01-04 | Helene Curtis, Inc. | Hair treatment compositions containing amidopolyether functional silicone |
| US6015574A (en) | 1997-06-09 | 2000-01-18 | L'oreal | Lipophilic carrier systems |
| US6228352B1 (en) | 1991-06-07 | 2001-05-08 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Hair styling agents and compositions containing hydrophobic hair styling polymers |
-
2001
- 2001-09-17 US US09/954,834 patent/US6566313B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Patent Citations (48)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3990991A (en) | 1974-02-01 | 1976-11-09 | Revlon, Inc. | Shampoo conditioner formulations |
| US4321156A (en) | 1977-03-30 | 1982-03-23 | S. C. Johnson & Son, Inc. | Shampoo composition |
| US4298494A (en) | 1979-03-27 | 1981-11-03 | Lever Brothers Company | Shampoo |
| US4321256A (en) | 1979-07-19 | 1982-03-23 | Lever Brothers Company | Shampoo containing a polyglycol-polyamine condensation resin and a phosphate ester |
| US4701322A (en) | 1980-04-21 | 1987-10-20 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Conditioning shampoo |
| US4479893A (en) | 1981-10-28 | 1984-10-30 | Kao Corporation | Shampoo composition containing phosphoric acid ester and organic silicon derivative |
| US4722837A (en) | 1984-05-29 | 1988-02-02 | Derma-Cure, Inc. | Medicated shampoo composition |
| US4741855A (en) | 1984-11-09 | 1988-05-03 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Shampoo compositions |
| US4726945A (en) | 1986-06-17 | 1988-02-23 | Colgate-Palmolive Co. | Hair rinse conditioner |
| US4728457A (en) | 1986-08-25 | 1988-03-01 | The Proctor & Gamble Company | Process for making a silicone-containing shampoo |
| US5091171B1 (en) | 1986-12-23 | 1995-09-26 | Ruey J Yu | Amphoteric compositions and polymeric forms of alpha hydroxyacids, and their therapeutic use |
| US5091171B2 (en) | 1986-12-23 | 1997-07-15 | Tristrata Inc | Amphoteric compositions and polymeric forms of alpha hydroxyacids and their therapeutic use |
| US5091171A (en) | 1986-12-23 | 1992-02-25 | Yu Ruey J | Amphoteric compositions and polymeric forms of alpha hydroxyacids, and their therapeutic use |
| US5059414A (en) | 1988-07-01 | 1991-10-22 | Shiseido Co. Ltd. | Multi-phase high viscosity cosmetic products |
| US4906460A (en) | 1988-08-05 | 1990-03-06 | Sorenco | Additive for hair treatment compositions |
| US4938953A (en) | 1988-08-09 | 1990-07-03 | The Upjohn Company | Self-preserving conditioning shampoo formulation |
| US5077041A (en) | 1989-04-14 | 1991-12-31 | Kao Corporation | Shampoo composition |
| US5120531A (en) | 1990-04-06 | 1992-06-09 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Hair styling conditioners |
| US5145607A (en) | 1990-06-19 | 1992-09-08 | Takasago International Corporation (U.S.A.) | Optically clear conditioning shampoo comprising anionic and cationic surfactants |
| US5078990A (en) | 1990-07-13 | 1992-01-07 | Helene Curtis, Inc. | Shampoos and conditioning shampoos having increased capacity for incorporation of conditioning agents and removal of hair soil |
| US5137715A (en) | 1990-12-07 | 1992-08-11 | Helene Curtis, Inc. | Hair shampoo-conditioner composition |
| US5334325A (en) | 1991-01-23 | 1994-08-02 | S. C. Johnson & Son, Inc. | Delayed-gelling, post-foaming composition based upon alkoxylated alkyl phosphate ester surfactants |
| US6228352B1 (en) | 1991-06-07 | 2001-05-08 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Hair styling agents and compositions containing hydrophobic hair styling polymers |
| US5217711A (en) | 1991-10-16 | 1993-06-08 | Mariana De Oliveira | Hair care system |
| US5384114A (en) | 1992-03-27 | 1995-01-24 | Helene Curtis, Inc. | Opacifier for water-based compositions |
| US5562898A (en) | 1992-03-27 | 1996-10-08 | Helene Curtis, Inc. | Opacifier for water-based compositions |
| US5393519A (en) | 1992-03-27 | 1995-02-28 | Helene Curtis, Inc. | Shampoo compositions |
| US5587154A (en) | 1992-03-27 | 1996-12-24 | Helene Curtis, Inc. | Shampoo compositions and suspending agent therefor |
| US5665267A (en) | 1992-03-27 | 1997-09-09 | Helene Curtis, Inc. | Shampoo compositions and suspending agent therefor |
| US5227156A (en) | 1992-04-14 | 1993-07-13 | Amway Corporation | Use of zinc compounds to stabilize a thiazolinone preservative in an anti-dandruff shampoo |
| US5456863A (en) | 1992-04-15 | 1995-10-10 | Helene Curtis, Inc. | Conditioning shampoo composition and method of preparing and using the same |
| US5578560A (en) | 1992-10-14 | 1996-11-26 | Henkel Corporation | Water-containing detergent mixtures comprising oligoglycoside surfactants |
| US5328685A (en) | 1993-03-30 | 1994-07-12 | Helene Curtis, Inc. | Clear conditioning composition |
| US5556615A (en) | 1993-03-30 | 1996-09-17 | Helene Curtis, Inc. | Clear conditioning composition |
| US5565216A (en) | 1993-07-21 | 1996-10-15 | Carson Products Company | Hair relaxer compositions |
| US5346639A (en) | 1994-01-11 | 1994-09-13 | Geoff Hatfield | Spray dispensed shampoo |
| US5610187A (en) | 1994-08-05 | 1997-03-11 | Witco Corporation | Biodegradable quaternary hair and skin conditioners |
| US5658558A (en) | 1994-10-03 | 1997-08-19 | Rohm And Haas Company | Hair styling compositions and method of enhancing the performance of hair fixative resins |
| US5883068A (en) | 1994-10-04 | 1999-03-16 | Henkel Kommanditgesellschaft Auf Aktien | Pumpable water-containing surfactant concentrates |
| US5618522A (en) | 1995-01-20 | 1997-04-08 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Emulsion compositions |
| US5683683A (en) | 1995-09-21 | 1997-11-04 | Helene Curtis, Inc. | Body wash composition to impart conditioning properties to skin |
| US5955066A (en) | 1995-10-16 | 1999-09-21 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Conditioning shampoo compositions having improved stability |
| US5977038A (en) | 1996-08-05 | 1999-11-02 | Helene Curtis, Inc. | Shampoo compositions and method |
| US5783200A (en) | 1997-01-21 | 1998-07-21 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Personal cleansing compositions |
| US6010689A (en) | 1997-04-21 | 2000-01-04 | Helene Curtis, Inc. | Hair treatment compositions containing amidopolyether functional silicone |
| US6015574A (en) | 1997-06-09 | 2000-01-18 | L'oreal | Lipophilic carrier systems |
| US5925615A (en) | 1998-03-06 | 1999-07-20 | Nu Skin International, Inc. | Awapuhi (Zingiber zerumbet) -containing hair cleansing and conditioning compositions |
| US5945093A (en) | 1998-04-22 | 1999-08-31 | Amway Corporation | Conditioning shampoo |
Cited By (56)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6780825B2 (en) * | 2001-02-06 | 2004-08-24 | Playtex Products, Inc. | Cleansing compositions with milk protein and aromatherapy |
| US20060034778A1 (en) * | 2002-09-27 | 2006-02-16 | Yoshinhisa Kitano | Packaged personal care compositions |
| WO2004104147A1 (en) * | 2003-05-22 | 2004-12-02 | Reckitt Benckiser N.V. | Aqueous cleaning compositions |
| US8535651B2 (en) | 2004-04-19 | 2013-09-17 | Wsp Chemicals & Technology, Llc | Water soluble polymer complexes with surfactants |
| US8211414B2 (en) * | 2004-04-19 | 2012-07-03 | Wsp Chemicals & Technology, Llc | Water soluble polymer complexes with surfactants |
| US20050276778A1 (en) * | 2004-04-19 | 2005-12-15 | Wsp Chemicals & Technology, Llc | Water soluble polymer complexes with surfactants |
| US7449203B2 (en) | 2004-06-30 | 2008-11-11 | E-L Management Corporation | Cosmetic compositions and methods comprising Rhodiola rosea |
| US20080268074A1 (en) * | 2004-06-30 | 2008-10-30 | Goldstein Mindy S | Cosmetic Compositions and Methods Comprising Rhodiola Rosea |
| US20060002871A1 (en) * | 2004-06-30 | 2006-01-05 | Goldstein Mindy S | Cosmetic compositions and methods comprising rhodiola rosea |
| US20100297042A1 (en) * | 2004-06-30 | 2010-11-25 | Goldstein Mindy S | Cosmetic Compositions and Methods Comprising Rhodiola Rosea |
| US8993506B2 (en) | 2006-06-12 | 2015-03-31 | Rhodia Operations | Hydrophilized substrate and method for hydrophilizing a hydrophobic surface of a substrate |
| US20080028986A1 (en) * | 2006-06-12 | 2008-02-07 | Rhodia, Inc. | Hydrophilized substrate and method for hydrophilizing a hydrophobic surface of a substrate |
| CN101100630B (en) * | 2006-07-07 | 2012-02-29 | 味之素株式会社 | Low temperature stable lacteous detergent composition |
| US20080008672A1 (en) * | 2006-07-07 | 2008-01-10 | Ajinomoto Co. Inc. | Low temperature-stable creamy wash composition |
| US7947260B2 (en) * | 2006-07-07 | 2011-05-24 | Ajinomoto Co., Inc. | Low temperature-stable creamy wash composition |
| WO2008047248A2 (en) * | 2006-10-19 | 2008-04-24 | L'oreal | Aqueous delivery system for water-insoluble materials |
| WO2008047248A3 (en) * | 2006-10-19 | 2009-12-10 | L'oreal | Aqueous delivery system for water-insoluble materials |
| US20080176977A1 (en) * | 2007-01-23 | 2008-07-24 | John Pastorello | Burst resistant bubbles |
| WO2008157193A3 (en) * | 2007-06-12 | 2009-02-26 | Rhodia | Mono-di-and polyol phosphate esters in personal care formulations |
| US20090123407A1 (en) * | 2007-06-12 | 2009-05-14 | Rhodia Inc. | Mono-, di- and polyol phosphate esters in personal care formulations |
| US20080312341A1 (en) * | 2007-06-12 | 2008-12-18 | Rhodia Inc. | Mono-, di- and polyol phosphate esters in personal care formulations |
| JP2010529206A (en) * | 2007-06-12 | 2010-08-26 | ローディア インコーポレイティド | Mono-, di- and polyol phosphate esters in personal care formulations |
| AU2008266168B2 (en) * | 2007-06-12 | 2014-07-10 | Rhodia Inc. | Mono-di-and polyol phosphate esters in personal care formulations |
| US20090124525A1 (en) * | 2007-06-12 | 2009-05-14 | Rhodia Inc. | Hard surface cleaning composition with hydrophilizing agent and method for cleaning hard surfaces |
| US7867963B2 (en) | 2007-06-12 | 2011-01-11 | Rhodia Inc. | Mono-, di- and polyol phosphate esters in personal care formulations |
| US7919449B2 (en) | 2007-06-12 | 2011-04-05 | Rhodia Operations | Detergent composition with hydrophilizing soil-release agent and methods for using same |
| US7919073B2 (en) | 2007-06-12 | 2011-04-05 | Rhodia Operations | Mono-, di- and polyol alkoxylate phosphate esters in oral care formulations and methods for using same |
| US20080312118A1 (en) * | 2007-06-12 | 2008-12-18 | Rhodia Inc. | Hard surface cleaning composition with hydrophilizing agent and method for cleaning hard surfaces |
| CN101679916B (en) * | 2007-06-12 | 2013-03-20 | 罗迪亚公司 | Mono-di-and polyol phosphate esters in personal care formulations |
| US8293699B2 (en) | 2007-06-12 | 2012-10-23 | Rhodia Operations | Hard surface cleaning composition with hydrophilizing agent and method for cleaning hard surfaces |
| US20080311055A1 (en) * | 2007-06-12 | 2008-12-18 | Rhodia Inc. | Mono-, di- and polyol alkoxylate phosphate esters in oral care formulations and methods for using same |
| US8268765B2 (en) | 2007-06-12 | 2012-09-18 | Rhodia Operations | Mono-, di- and polyol phosphate esters in personal care formulations |
| US20090023618A1 (en) * | 2007-07-20 | 2009-01-22 | Rhodia Inc. | Method for recovering crude oil from a subterranean formation |
| US20100260696A1 (en) * | 2007-08-02 | 2010-10-14 | Clariant Finance (Bvi) Limited | Aqueous Compositions Containing Alkoxylated Phosphoric Acid Triesters |
| US20100008885A1 (en) * | 2008-07-09 | 2010-01-14 | Susan Daly | Methods and kits imparting benefits to keratin-containing substrates |
| WO2010031689A1 (en) * | 2008-09-17 | 2010-03-25 | Henkel Ag & Co. Kgaa | All-purpose cleaner with improved cleaning performance in diluted application |
| US20120145172A1 (en) * | 2009-08-31 | 2012-06-14 | Kobo Products, Inc. | Surface modified pigment |
| US11453598B2 (en) | 2009-08-31 | 2022-09-27 | Colgate-Palmolive Company | Surface modified pigment |
| US20150094383A1 (en) * | 2012-04-24 | 2015-04-02 | Stepan Company | Synergistic surfactant blends |
| US10982174B2 (en) | 2012-04-24 | 2021-04-20 | Stepan Company | Synergistic surfactant blends |
| US9688944B2 (en) * | 2012-04-24 | 2017-06-27 | Stepan Company | Synergistic surfactant blends |
| US10513670B2 (en) | 2012-04-24 | 2019-12-24 | Stepan Company | Synergistic surfactant blends |
| US9622951B2 (en) | 2012-10-29 | 2017-04-18 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Personal care compositions |
| CN105906526A (en) * | 2016-04-25 | 2016-08-31 | 中国石油集团渤海钻探工程有限公司 | Technology for preparing acidized self-diverting agent by batch process |
| CN111225655A (en) * | 2017-08-25 | 2020-06-02 | 荷兰联合利华有限公司 | Personal cleansing compositions |
| US20210069079A1 (en) * | 2017-08-25 | 2021-03-11 | Conopco, Inc., D/B/A Unilever | Personal cleansing composition |
| CN111246837A (en) * | 2017-08-25 | 2020-06-05 | 荷兰联合利华有限公司 | Personal cleansing compositions |
| US11779528B2 (en) * | 2017-08-25 | 2023-10-10 | Conopco, Inc. | Personal cleansing composition |
| US11931442B2 (en) * | 2017-08-25 | 2024-03-19 | Conopco, Inc. | Personal cleansing composition |
| US20190216697A1 (en) * | 2018-01-18 | 2019-07-18 | Nohbo,LLC | Hygiene product pod and methods of using same |
| US11744786B2 (en) | 2018-01-18 | 2023-09-05 | Nohbo, Inc. | Hygiene product pod and methods of using same |
| US20210000724A1 (en) * | 2019-07-05 | 2021-01-07 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Personal care cleaning compositions |
| US11813345B2 (en) * | 2019-07-05 | 2023-11-14 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Personal care cleaning compositions |
| US11045397B2 (en) | 2019-11-06 | 2021-06-29 | Nohbo, LLC | Hygiene product pod and methods of using same |
| WO2021104844A1 (en) | 2019-11-26 | 2021-06-03 | Unilever Ip Holdings B.V. | Cleansing composition |
| WO2024002647A1 (en) | 2022-06-30 | 2024-01-04 | Unilever Ip Holdings B.V. | Stable wash composition with unsaturated zwitterionic surfactant |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US6566313B1 (en) | Shampoo and body wash composition and method of use thereof | |
| JP6449544B2 (en) | Cleaning composition | |
| US5939059A (en) | Hair conditioner and 2 in 1 conditioning shampoo | |
| AU2002300400B2 (en) | Moisturizing Detergent Compositions | |
| ES2435741T3 (en) | Conditioning composition | |
| US5576279A (en) | Stable conditioning shampoo containing an anionic surfactant a fatty alcohol, and polyethyleneimine | |
| US20030228272A1 (en) | Novel antidandruff conditioning shampoo | |
| EP2512425B1 (en) | Cleansing composition | |
| AU678450B2 (en) | Stable conditioning shampoo containing an anionic surfactant, a fatty alcohol, a silicone conditioner and polyethyleneimine | |
| US10945935B2 (en) | Shampoo composition containing a gel network | |
| EP3474811B1 (en) | Shampoo composition containing a gel network | |
| KR20060105522A (en) | Detergent cosmetic compositions comprising three surfactants and a fatty ester, and use thereof | |
| EP2770975B1 (en) | Cleansing composition | |
| EP0965322A1 (en) | Hair cleansing composition and personal cleansing composition with low skin irritancy | |
| EP2717841B1 (en) | Cleansing composition | |
| EP2600827B1 (en) | Cleansing composition | |
| JPH04230614A (en) | Hair cosmetic | |
| US6774095B2 (en) | Detergent composition | |
| PL199430B1 (en) | Cleansing cosmetic compositions and use | |
| US6538011B1 (en) | Composition for the antidandruff treatment of the hair and scalp based on an antidandruff active principle and on a hydroxy acid | |
| EP2600826B1 (en) | Cleansing composition | |
| WO1998000487A1 (en) | Cleansing compositions | |
| GB2613446A (en) | Compositions and methods | |
| JPH07258689A (en) | Liquid cleaning agent composition |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| AS | Assignment |
Owner name: HENKEL CORPORATION, PENNSYLVANIA Free format text: ASSIGNMENT OF ASSIGNORS INTEREST;ASSIGNORS:HOHENSTEIN, KAREN A.;ANDRASSY, GEORGE;REEL/FRAME:012642/0125 Effective date: 20011214 |
|
| STCF | Information on status: patent grant |
Free format text: PATENTED CASE |
|
| CC | Certificate of correction | ||
| FPAY | Fee payment |
Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| AS | Assignment |
Owner name: HENKEL CONSUMER GOODS INC., ARIZONA Free format text: ASSIGNMENT OF ASSIGNORS INTEREST;ASSIGNOR:HENKEL CORPORATION;REEL/FRAME:023668/0315 Effective date: 20050801 |
|
| FPAY | Fee payment |
Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| FPAY | Fee payment |
Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| AS | Assignment |
Owner name: HENKEL US IV CORPORATION, CONNECTICUT Free format text: ASSIGNMENT OF ASSIGNORS INTEREST;ASSIGNOR:HENKEL CONSUMER GOODS, INC.;REEL/FRAME:041218/0812 Effective date: 20161231 |
|
| AS | Assignment |
Owner name: HENKEL IP & HOLDING GMBH, GERMANY Free format text: ASSIGNMENT OF ASSIGNORS INTEREST;ASSIGNOR:HENKEL US IV CORPORATION;REEL/FRAME:042108/0150 Effective date: 20170328 |